3DKnITS: Three-dimensional Digital Knitting of Intelligent Textile Sensor for Activity Recognition and Biomechanical Monitoring
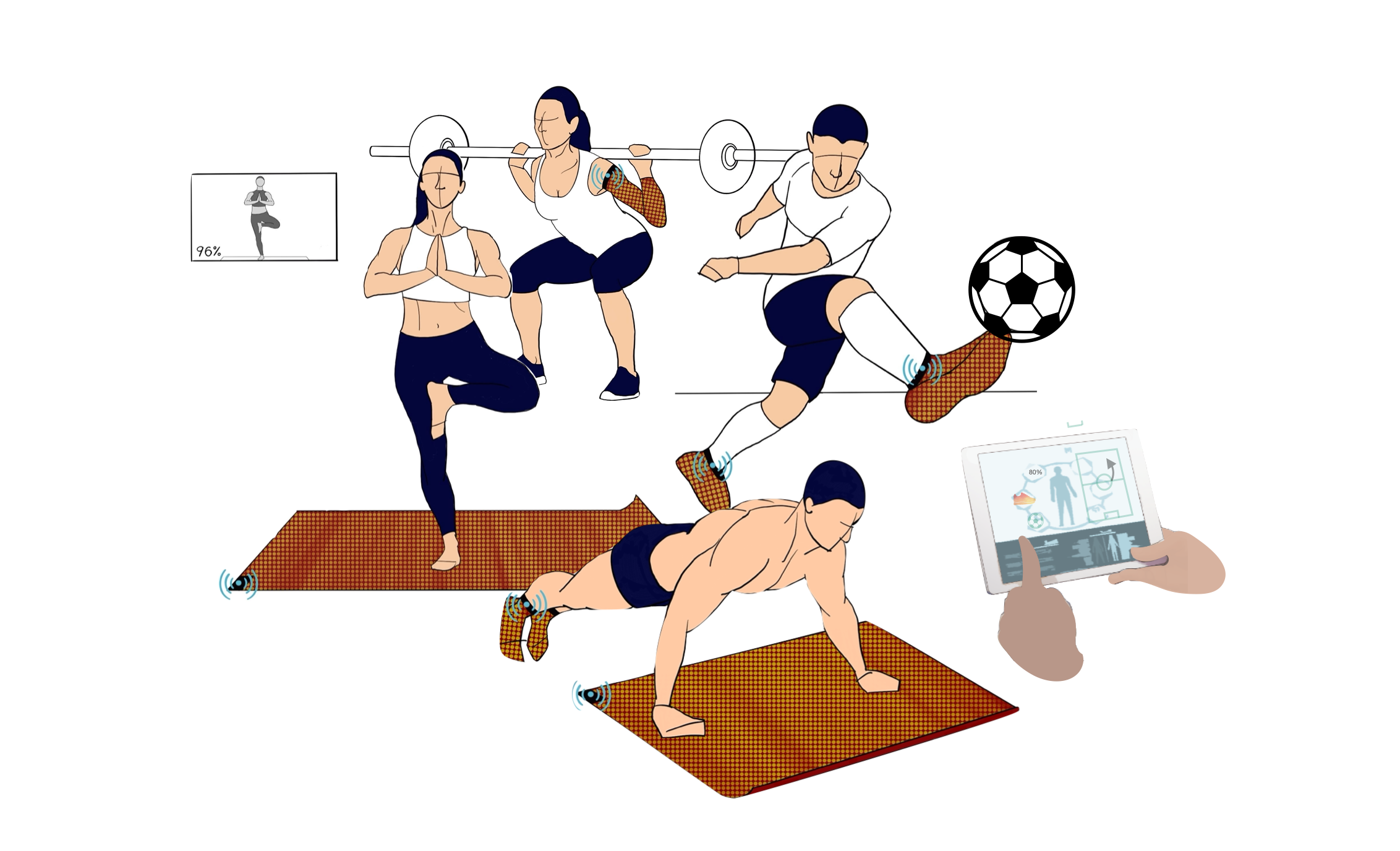
We present an approach to develop seamless and scalable piezo-resistive matrix-based intelligent textile using digital flat-bed and circular knitting machines. By combining and customizing functional and common yarns, we can design the aesthetics and architecture and engineer both the electrical and mechanical properties of a sensing textile. We propose a method to shape and personalize three-dimensional piezo-resistive textile that can conform to the human body through thermoforming principles with melting yarns. It results in a robust textile structure and intimate interfacing, suppressing sensor drifts and maximizing accuracy while ensuring comfortability.
The digital knitting approach enables the fabrication of 2D to 3D pressure-sensitive textile interiors and wearables, including a 45 x 45 cm intelligent mat with 256 pressure-sensing pixels, and a circularly-knitted, form-fitted shoe with 96 sensing pixels across its 3D surface. Furthermore, we have designed a visualization tool and a framework that treats the spatial sensor data as image frames. Our personalized convolutional neural network models are able to classify 7 basic activities and exercises and 7 yoga poses in-real time with 99.6% and 98.7% accuracy respectively. Further, we demonstrate our technology for a variety of applications ranging from rehabilitation and sport science, to wearables and gaming interfaces.
Publications Wicaksono, I., Hwang, P. G., Droubi, S., Wu, F. X., Serio, A. N., Yan, W., and Paradiso, J.A., 2022. 3DKnITS: Three-dimensional Digital Knitting of Intelligent Textile Sensor for Activity Recognition and Biomechanical Monitoring. IEEE in Medicine and Biology Society.
Coverage MITNews | Popular Science | Medgadget | World Economic Forum | InnovationInTextiles | Communications of the ACM | Materials Today
Core77 FastCompany Innovation by Design Award Finalist 2022.
Smart textiles that can sense how users are moving could be useful in healthcare, for example, for monitoring gait or movement after an injury. Athletes could donn them to receive feedback on their movements, or they could be used to create a better video game interface.
Full story via Popular Science